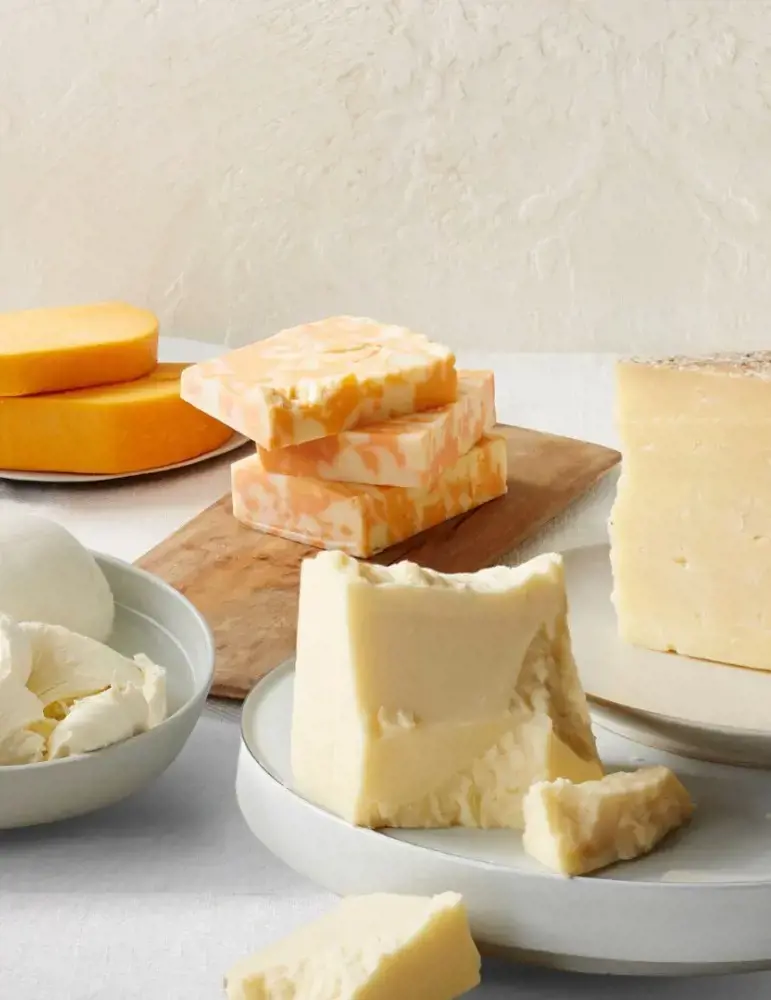
20 Types Of Cheese And Their Nutrition Values

This post may contain affiliate links. If you make a purchase through links on our site, we may earn a commission.
From grilled cheese to chili paneer, cheese is used in thousands of ways. It is so versatile that every country has its own version.
Apart from its versatility in various dishes and addictive taste, cheese comes with several health benefits. It is rich in essential nutrients with high amounts of saturated fat. Here are 20 types of cheese and the nutritional value of cheese.
1. American Cheese
American cheese, unlike other cheeses made with milk, is processed and made with a combination of cheeses like cheddar and Colby jack. It is a mainstay in the U.S. and can be found everywhere, from the deli counters to the supermarkets.
The taste and texture vary depending on the cheese used and additives. Also, the color ranges from orange and yellow to white, depending on the manufacturer.
2. Ricotta
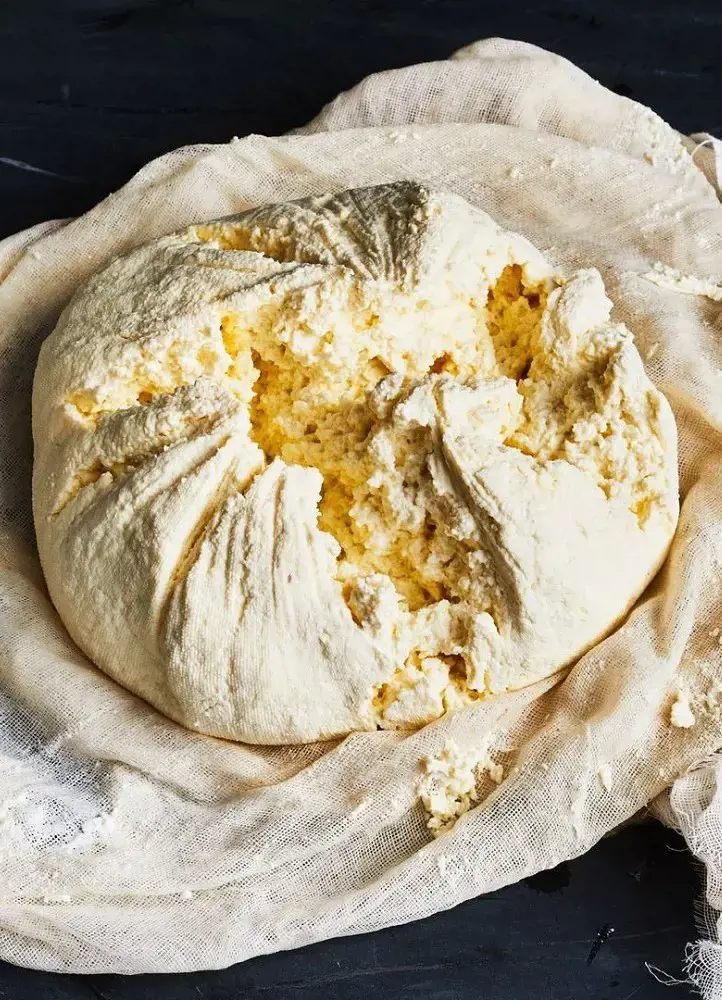

Ricotta is a fresh, non-aged cheese made from whey, a liquid left over after milk is curdled and strained. It usually comes from the milk of sheep.
The whey is heated until the curds and whey separate, and the curds are cooked again to create this cheese. It has a slightly sweet, and creamy texture.
Ricotta is also an excellent source of protein, as it contains all nine essential amino acids. The cheese is high in calories but offers much nutritional value thanks to its essential vitamins and minerals.
3. Mozzarella
Mozzarella is a curd cheese from southern Italy. It is traditionally made from buffalo milk. The milk is cooked with animal rennet, a substance derived from the stomach lining of unweaned young animals.
This causes the curds and whey to separate. The curd is then melted and stretched in hot water to form mozzarella.
Mozzarella is known for its smooth, shiny surface, porcelain color, and delicate milky flavor. It is soft and elastic, allowing it to be easily pulled apart or stretched. The cheese is lower in sodium and calories than other cheeses, making it healthier.
4. Burrata
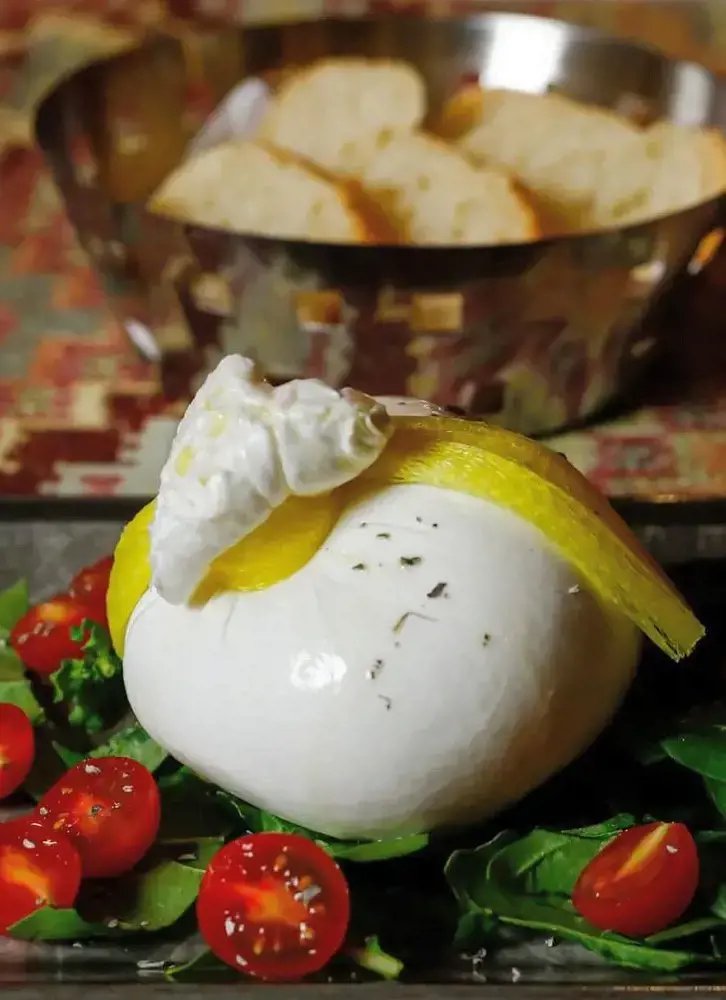

During the production of mozzarella, there were lots of mozzarella curds left over. Cheese artisans did not want to waste them, so they combined the remnants with fresh cream and encased the mixture in a delicate pouch of mozzarella.
This innovative technique led to the birth of Burrata. From the outside, it looks just like mozzarella, but once you stab it, the luscious, rich, creamy center oozes out.
Burrata has a higher calorie and sodium content than mozzarella because of the cream, but it still offers many nutritional benefits. However, it should be eaten moderately.
5. Brie
Brie is a soft, creamy, buttery cheese named after the region where it was first created. It is made from cow’s milk, rennet, and cheese cultures or bacteria used in cheese making.
This mixture goes through a lactic fermentation process, causing white mold to form on the rind of the cheese. Unlike other molds, this one is safe to eat.
It has all the common cheese nutrients but with the addition of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA).
6. Feta
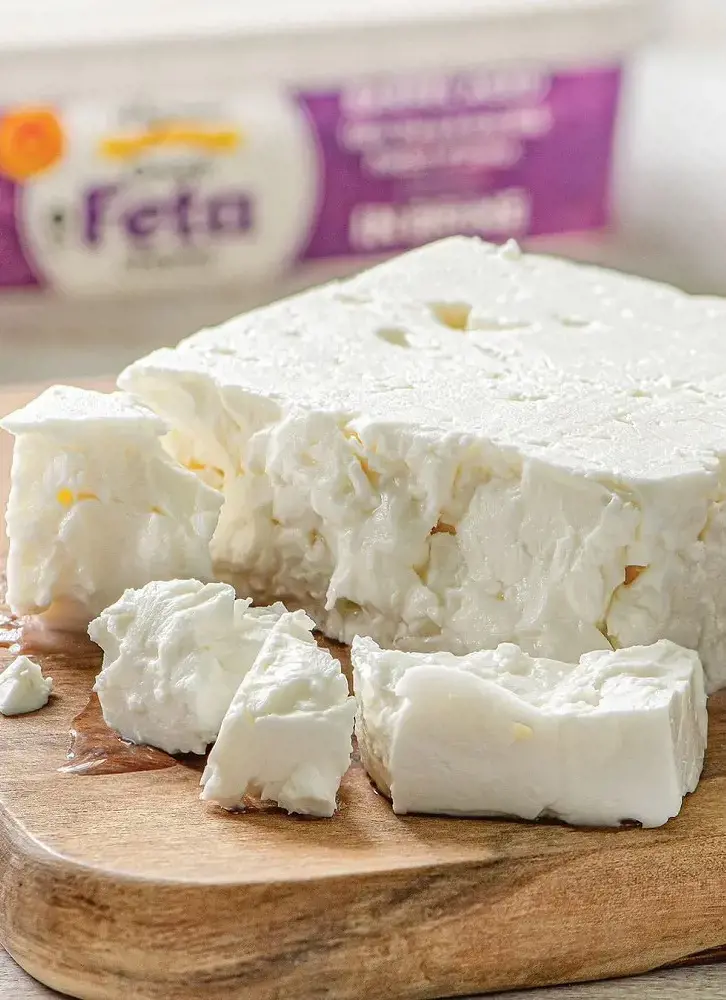

Feta, a staple in Greek cuisines, is a fresh, white-brined cheese. It is made from a combination of goat’s and sheep’s milk. This particular combination gives feta its unique taste.
The sheep’s milk gives it a sharp acidic flavor, while the goat’s milk makes it mild and palatable. This cheese is suitable for people who are intolerant to cow’s milk.
Like Brie, feta also contains CLA, which offers many benefits, including weight loss. According to a 2019 analysis, people with obesity who took 3 g of a CLA supplement each day for three months experienced decreased body fat mass than those who did not.
7. Cream Cheese
Cream cheese is a soft, mild-tasting cheese made from cow’s milk and cream. It is made with curds from fermented milk, cream, and lactic acid.
The curds are heated, after which stabilizers are added to make the cream cheese. It has a slightly sweet and tangy taste with a hint of lactic aroma.
The lactic acid contains bacteria, some of which are probiotics. These probiotics offer health benefits, such as maintaining a healthy gut, boosting our immune system, and reducing inflammation in the body.
8. Gorgonzola
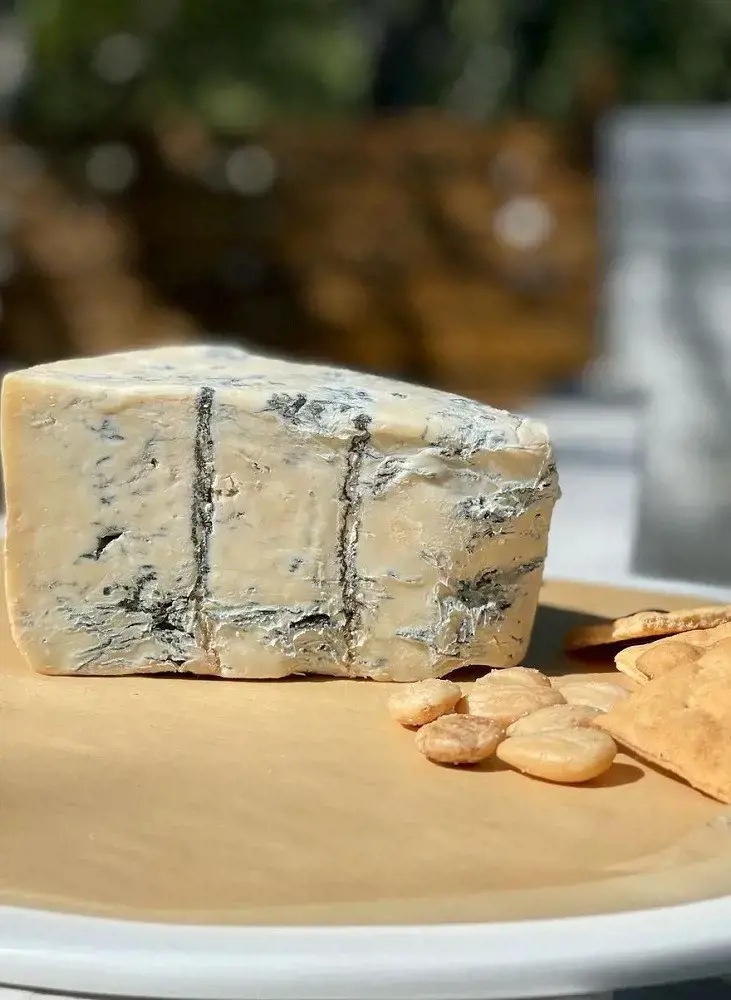

Gorgonzola is a type of blue cheese that hails from Italy. Like most cheeses, it starts with milk, but for gorgonzola, it is strictly cow milk.
The milk is mixed with Penicillium roqueforti, a fungal starter culture, and other cultures to extract the curds. These curds are pressed and tucked away for fermentation.
During the fermentation, metal rods are used to create air channels in the cheese that enable the blue mold to grow. This creates the distinctive blue-green veins on the gorgonzola.
9. Chevre
Chevre refers to any cheese made from goat’s milk. It is aged for two to three days or weeks, depending on the consistency and flavor you want. Fresh chevre is soft and creamy with a mild, buttery flavor.
As the cheese ages, it becomes drier and crumbly with a strong tangy taste. This type of cheese is highly nutritious and has more medium-chain fatty acids than cheese from cow’s milk.
Due to their shorter length, these fatty acids digest faster and are absorbed rapidly into the body. This could help reduce body weight and prevent obesity.
10. Cottage Cheese
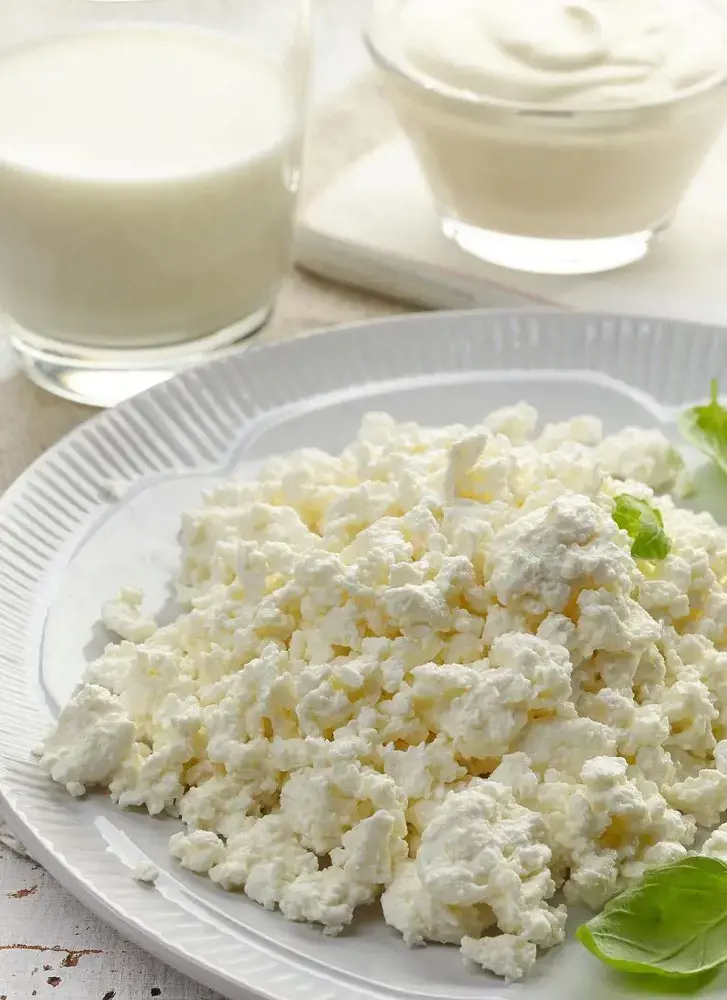

Cottage cheese is soft, white, and creamy and does not undergo an aging or ripening process. It is made by coagulating milk with acid, resulting in curdled milk. The curds are separated and cooked to release moisture, which results in a sweet and crumbly cottage cheese.
Cottage cheese is high in protein, like most cheeses, and offers many benefits. It can help reduce the risk of developing insulin resistance, which is associated with diabetes. It can also help improve bone health and provide antioxidant protection.
11. Cheddar
There are many types of cheddar cheese, depending on how long it is aged and wrapped. Regardless of the type, making cheddar is similar to other cheeses.
A young cheddar, aged for less than six months, has a smoother texture and creamier and less tart flavor than one aged for at least a year.
Cheddar is rich in protein and calcium. Additionally, it is an excellent source of vitamin K2, which is important for heart and bone health.
12. Queso Blanco
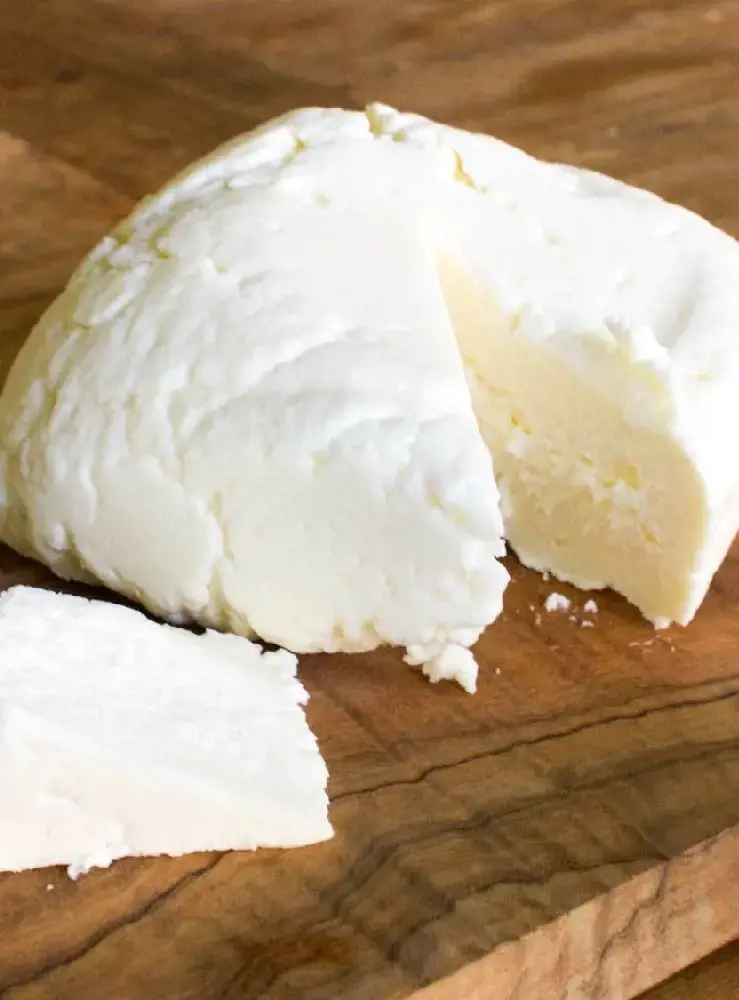

Queso Blanco, or white cheese in Spanish, is a soft and crumbly cheese made of pure cow’s milk or a combination of cow and goat’s milk. Unlike other cheeses that are aged, queso blanco is fresh. The cheese curds are aged for three days before it is consumed.
Homemade queso blanco does not hold very long, but the ones found in grocery stores do because it is vacuum-sealed in plastic.
It has a mild, milky flavor with a crumbly texture that gets smooth and creamy upon heating. It is also healthier than other cheeses because of its lower sodium and fat content.
13. Camembert
Camembert is soft, surface-ripened cheese made from cow’s milk. It is often mistaken for a Brie. Both of them have a bloomy edible rind with a soft ivory-colored center.
However, the flavor profile and aroma are slightly different. Camembert has an earthy scent, while Brie has a light buttery aroma. They could taste similar as well, but there is a subtle difference.
Camembert has an earthy flavor and a dense texture, while Brie has a soft and creamy mouthfeel. Despite the differences, both are equally healthy. Camembert is a vital source of calcium, phosphorus, and other wide range of essential minerals.
14. Swiss Cheese
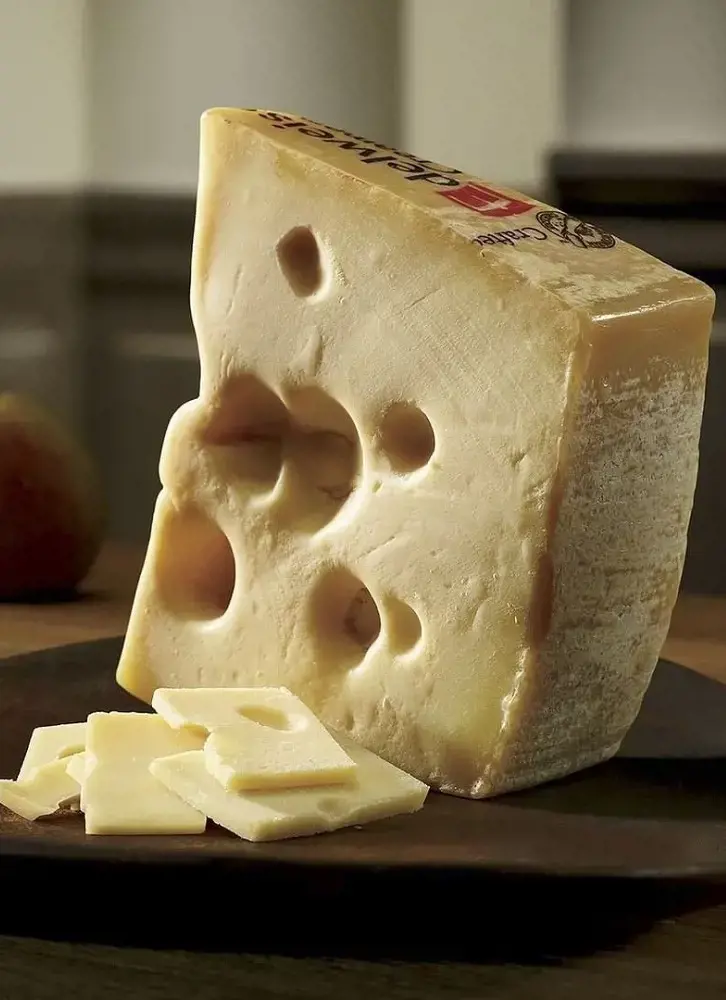

Swiss cheese is a generic name given to all the cheeses that Switzerland makes. There are countless types of Swiss cheese, but the most popular one is the Emmental, a semi-hard cheese with distinctive holes of varying sizes.
Most Swiss cheeses are produced under the strict Appellation d’Origine Protégée (AOP) standards or Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) in Switzerland.
These cheeses start with cow’s milk, making them high in calcium and protein. They also deliver a healthy dose of vitamin B12 and have comparatively less salt than other cheeses.
15. Parmesan
Parmesan Parmigiano, or simply Parmesan, is an Italian hard cheese made from skimmed or partially skimmed cow’s milk.
It has a slightly sweet and nutty flavor that can be bitter in inferior quality Parmesan. It also has a crumbly and gritty texture and may vary in color from pale to bright yellow.
Unlike other cheeses, Parmesan has a Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) set by the European Union. This cheese is suitable for lactose intolerant, as it is virtually lactose-free.
16. Raclette
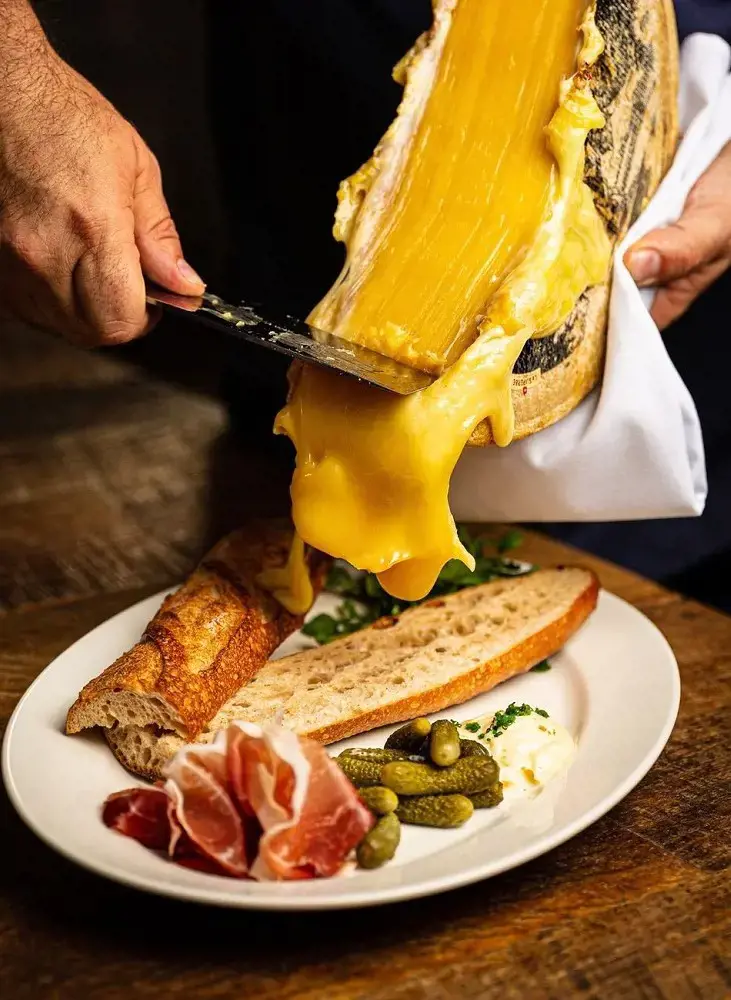

Raclette, meaning “to scrape” in French, is a semi-hard cheese produced in the French and Swiss Alps. It has a creamy texture, ivory-pale yellow pate with irregular holes, and an edible brownish-orange rind.
The flavor of raclette will vary slightly depending on where it is produced, but it usually has a nutty, slightly acidic, to milky flavor. It can be part of a healthy diet because it contains essential nutrients, but it is important to consume in moderation.
17. Grana Padano
Grana Padano is a hard cheese and a staple in Italy. It has a Protected Designation of Origin (PDO), and according to the PDO, production of Grana Padano is permitted in some provinces of Italy only.
It must be made with raw milk from cows that are milked twice a day. Also, Grana Padano can only be sold on the market after it has aged for nine months.
The name is Grana, meaning grainy in Italian, and reflects the cheese’s texture. It has a granular texture that becomes more crumbled as it ages.
18. Paneer
Paneer, sometimes known as Indian cottage cheese, is a staple in South Asian cuisines. It is a fresh cheese that does not melt and is made from cow or buffalo milk that is pasteurized, raw, whole, or skimmed.
The cheese is milky and has a mild taste. It has a firm and spongy texture, similar to cottage cheese and Italian ricotta.
Unlike some cheeses that melt upon contact with heat, paneer holds its shape, making it an excellent vehicle for sauces and marinades. The Indian cottage cheese is an excellent source of protein, vitamins, and minerals and is often substituted as meat by vegetarians.
19. Halloumi
Halloumi is a slightly springy, brined, semi-hard white cheese with roots in Cyprus. It is traditionally prepared from the milk of goats, sheep, or cows.
The Cypriot cheese has no rind and has a tangy and salty flavor. You can eat it raw, but it does not taste like much and has a rubbery texture.
Cooking the cheese also enhances the saltiness. Halloumi is a relatively healthy cheese, but with high sodium levels, it should be eaten moderately.
20. Washed Rind Cheese
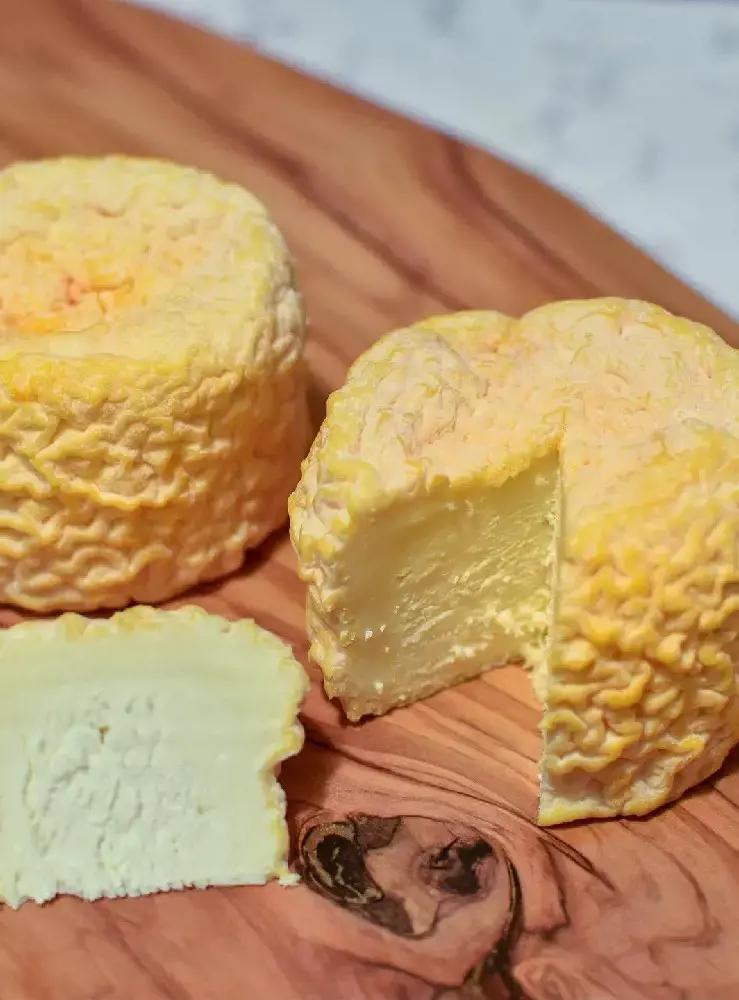

Washed rind cheese, as the name suggests, refers to cheese with a brine-washed (or moistened) rind. After the cheese is formed and matured, the rinds are washed with a brine solution containing bacteria called Brevibacterium Linens.
This process causes bacteria to grow on the surface of the cheese, which changes the smell and color of the cheese. The cheese rinds turn a reddish color and give off a pungent smell.
Washed rind cheese with a high moisture content is creamier than low moisture ones that are firmer. The flavors also vary from earthy and savory to yeasty and nutty.
Nutritional Value
Cheese contains many essential nutrients that our body needs. Different cheeses have different nutritional values, but one ounce of hard cheese, or a wedge about the size of your thumb, contains
- Calories: 120 calories
- Protein: 8 grams
- Saturated Fat: 6 grams
- Calcium: 180 milligrams
- Sodium: 300-450 mg per serving
- Fiber: 0 grams
- Sugar: 1 grams
Apart from these nutrients, most cheeses are high in vitamins A, D, K, and zinc which helps keep our bones healthy.
Recent posts
Nutrition
Nutrition
16 Benefits Of Coriander That Will Surprise You
Abundant in nutrients and antioxidants, coriander is an annual herb with a characteristic aroma that is extensively used around the world. Both coriander leaves (also called cilantro) and seeds are used in various cuisines around the world. Known fo...
Nutrition
Chia Seeds Benefits: 15 Reasons To Eat These Tiny Seeds
Chia seeds are tiny edible seeds obtained from the plant known as "Salvia hispanica", belonging to the mint family. Oval, gray, and filled with black and white spots, these small seeds are highly valued for their abundant nutrients and health be...
Nutrition
How Much Calcium Is Actually Needed?
Calcium is a mineral associated with bones, muscles and the nervous system in the body. Current dietary guidelines suggest different Recommended Dietary Allowances(RDAs) for adult males and females, with 1000mg being optimal for males and 1200mg for...
Nutrition
B12 Vitamin Food Sources: A Comprehensive Guide
Vitamin B12, an essential nutrient, plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including red blood cell production, nerve function, and DNA synthesis. While animal-based foods are the primary sources of B12, certain fortified plant-based foods...
Nutrition
What Foods Are High In Cholesterol? 20 Foods To Avoid
Animal products like meat, eggs, milk, and cheese are sources of dietary cholesterol, unlike plant-based foods. For those aiming to lower their cholesterol intake, it's essential to be mindful of animal-based food choices. While some high-cholesterol...
Nutrition
18 Fat Burning Smoothies For Weight Loss
The weight loss journey is tough if you have to get on the same path day after day, facing cravings and temptations along the way. We suggest you stop making it a monotonous struggle and make it a flavorful adventure instead. One of the easiest and m...







