15 Surprising Benefits Of Collagen

This post may contain affiliate links. If you make a purchase through links on our site, we may earn a commission.
Collagen is the most abundant protein playing a crucial role in the body's internal scaffolding to provide structure, strength, and elasticity to your connective tissues, bones, and muscles.
It's no wonder that collagen accounts for a whopping 30% of the protein in our bodies. It's the glue that binds our cells, the scaffolding that shapes our organs, and the shock absorber that cushions our joints.
In this article, we will explore the potential benefits of collagen to support your body's natural foundation for long-term health and well-being.
1. Joint Support
Collagen is a protein that plays a vital role in maintaining the health and function of your joints. As you age, your body's natural production of collagen declines, which can lead to joint pain, stiffness, and inflammation. Joint support collagen supplements are designed to help replenish your body's collagen stores and improve joint health.
Collagen can help to improve joint mobility and flexibility, making it easier to perform daily activities. It also has anti-inflammatory properties that can help to reduce inflammation in the joints. Supplementing with collagen may help reduce joint pain and stiffness associated with conditions like osteoarthritis.
2. Bone Strength
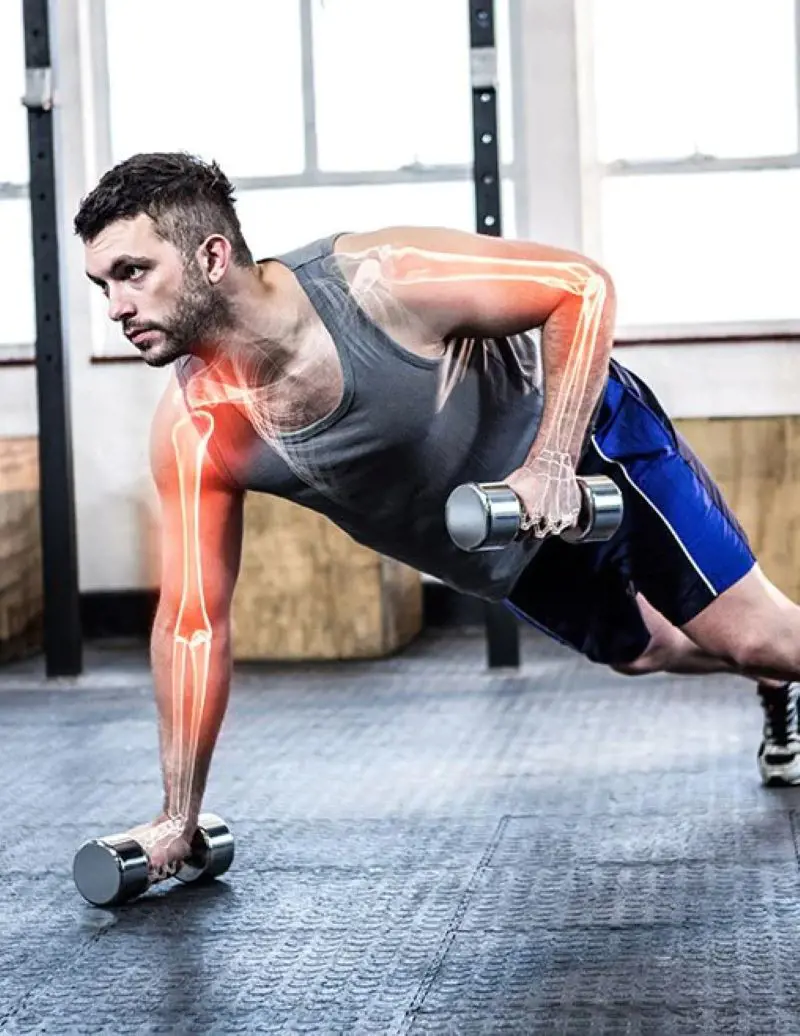

Collagen provides structural support to bones, helping to maintain bone density and prevent fractures and osteoporosis. It is indeed a crucial component of bones, providing them with structure and flexibility. However, your body naturally produces collagen throughout your life.
Certain studies in postmenopausal women and older adults found increased bone mineral density (BMD) with collagen supplementation compared to placebo. Also, collagen fibers in bone tissue provide flexibility and resilience, allowing bones to withstand impact and stress without fracturing. This flexibility is crucial for maintaining bone health and preventing fractures, particularly in older adults.
3. Muscle Mass

Collagen is indeed the most abundant protein in the body, making up around 30% of its protein content. It plays a crucial role in providing structure and support to various tissues, including muscles. Collagen fibers provide a framework for muscle cells to attach to and contract, contributing to overall muscle strength and function.
It plays a vital role in joint health and lubrication. Supplementing with collagen might help reduce joint pain and stiffness, which could indirectly improve exercise performance and facilitate muscle growth. Some studies suggest collagen peptides may help reduce muscle soreness and improve recovery after exercise, potentially allowing for more frequent and isometric exercises and intensive workouts.
4. Skin Health

Collagen fibers are the main structural component of the dermis, the middle layer of your skin. They provide support and elasticity, giving your skin its plumpness and youthful appearance. Studies suggest that collagen peptides may help increase skin hydration, leading to a plumper, more supple appearance.
Collagen helps reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines by providing support to the skin's structure. As collagen production declines with age, skin becomes less firm and elastic, leading to the formation of wrinkles and sagging skin. It also helps maintain skin hydration by retaining moisture within the skin's layers. Proper hydration is essential for keeping the skin plump, smooth, and radiant.
5. Tendon And Ligament Health

Tendons and ligaments, which attach muscles to bones and support joints, are largely made of collagen. Collagen supplements may aid in strengthening tendons and ligaments, lowering the chance of harm. Type I collagen, which is also present in skin and bones, makes up the majority of tendon and ligament composition. Collagen fibers offer structural support, suppleness, and strength.
While collagen provides strength and rigidity to tendons and ligaments, it also allows for flexibility and elasticity, enabling these tissues to stretch and recoil without tearing or rupturing. This flexibility is crucial for maintaining joint mobility and preventing injuries during movement.
6. Heart Health

Collagen is a major component of the heart's structure, including the blood vessels, heart valves, and inner lining. It provides strength, flexibility, and support to these vital tissues. Its production naturally declines with age, which can stiffen blood vessels and contribute to heart health problems like high blood pressure and atherosclerosis.
Its anti-inflammatory properties might benefit conditions like chronic inflammation, which is linked to an increased risk of heart disease. Collagen helps prevent excessive blood clot formation by promoting the formation of stable, well-organized blood clots when needed. Proper clot formation is essential for preventing excessive bleeding and maintaining cardiovascular health.
7. Hair Growth

Hair follicles, where hair grows, are embedded in the dermis, which is largely made up of collagen. Collagen provides structural support and nourishment to these follicles. It is composed of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. Keratin, the main protein in hair, requires specific amino acids found in collagen.
Collagen contributes to the elasticity of the skin, including the skin on the scalp. Improved scalp elasticity may support better blood circulation to the hair follicles, ensuring they receive essential nutrients for healthy growth. It also helps retain moisture in the skin, including the scalp. A well-moisturized scalp is essential for maintaining a healthy hair growth environment and preventing issues like dryness and flakiness, which can hinder hair growth.
8. Gut Health
Collagen, the most abundant protein in the body, plays a crucial role in various tissues, including the gut lining. This lining, also known as the intestinal barrier, acts as a gatekeeper, allowing essential nutrients to pass while keeping harmful substances out. However, factors like stress, diet, and certain medications can damage the gut lining, contributing to various digestive issues.
Collagen peptides, smaller fragments of collagen, might help repair and strengthen the gut lining, potentially improving its barrier function. This could benefit individuals with leaky gut syndrome or other gut-related conditions. Some research suggests collagen peptides might positively influence the gut microbiome, potentially promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and enhancement of overall gut health.
9. Wound Healing
Collagen, especially type I and III, forms the essential scaffolding that supports new tissue growth during wound healing. It provides the structural foundation for cells to migrate, proliferate, and rebuild damaged tissue. It plays a crucial role in wound healing, making it a valuable natural resource for the body's repair process.
Collagen fibers offer both strength to hold the wound together and flexibility to accommodate wound contraction and remodeling. It interacts with cells involved in healing, stimulating migration, proliferation, and differentiation to form new skin, blood vessels, and other tissues.
10. Bone Density
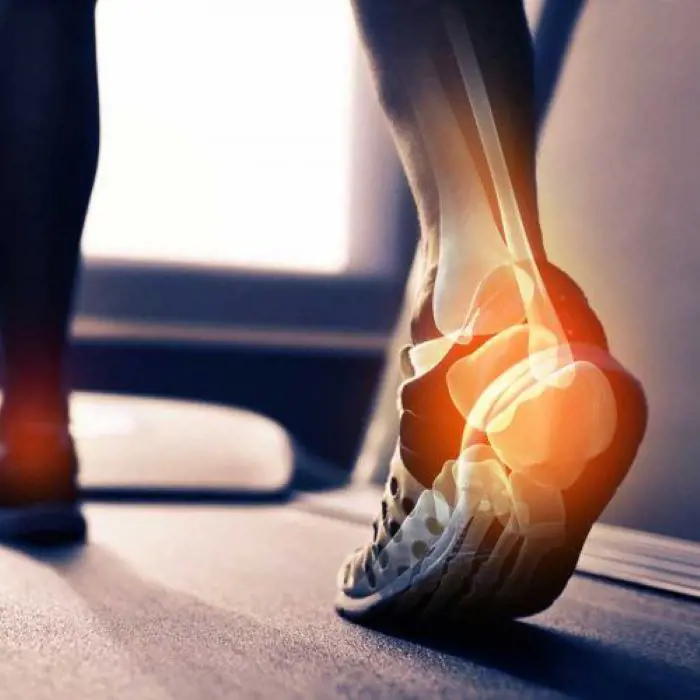

Collagen plays a crucial role in bone remodeling, the continuous process of bone resorption (breakdown) and formation. Osteoclasts, cells responsible for bone resorption, break down old or damaged bone tissue, while osteoblasts, cells responsible for bone formation, deposit new collagen and minerals to replace it. Collagen serves as a signaling molecule that directs the activity of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, coordinating the remodeling process and maintaining bone density.
Collagen is involved in the process of fracture healing, providing the structural framework for the formation of callus tissue and new bone growth. Collagen supplementation may help accelerate fracture healing and improve the quality of the healed bone tissue.
11. Anti-Inflammatory Properties

Collagen exhibits anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit various aspects of health. It contains amino acids such as glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline, which have anti-inflammatory properties. These amino acids help modulate the body's inflammatory response by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory molecules and promoting the synthesis of anti-inflammatory molecules.
Collagen aids in gastrointestinal tract inflammation reduction and gut integrity maintenance. Collagen aids in the prevention of toxic chemicals seeping into the circulation (leaky gut syndrome), which can lead to systemic inflammation and a host of other health problems. It does this by promoting the development and repair of the gut lining.
12. Improved Sleep Quality

A vital component of connective tissues, such as muscles, ligaments, and tendons, is collagen. Collagen supplements promote healthy joints and muscles, which may help lessen pain or discomfort that might disrupt sleep. Better mobility and comfort might result in fewer sleep disturbances and more restful sleep in general.
Collagen supports gut health by promoting gut barrier integrity and reducing inflammation in the digestive tract. The gut-brain axis plays a crucial role in regulating sleep-wake cycles and overall sleep quality. A healthy gut microbiome and balanced gut function can positively influence sleep patterns and cognitive function.
13. Balanced Blood Sugar Levels

Regulation of blood sugar levels is the secondary benefit of collagen. It is a source of dietary protein, which can help promote feelings of fullness and satiety. Including collagen-rich foods or supplements in meals or snacks may help reduce appetite and prevent overeating, leading to more stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Collagen is a major component of muscle tissue, and adequate muscle mass is important for glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. By supporting muscle health and function, collagen may indirectly contribute to balanced blood sugar levels. Strong, healthy muscles are more efficient at utilizing glucose for energy and regulating blood sugar levels.
14. Liver Health

Collagen is rich in the amino acid glycine, which plays a crucial role in liver function. Glycine is involved in the synthesis of glutathione, a powerful antioxidant that helps protect liver cells from oxidative damage and detoxify harmful substances. Adequate glycine intake may support liver detoxification pathways and promote overall liver health.
Some studies suggest collagen peptides may have anti-inflammatory properties, which could potentially benefit conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Collagen provides the structural framework for tissue repair and regeneration. In cases of liver injury or damage, collagen plays a crucial role in the formation of scar tissue and the regeneration of liver cells.
15. Eye Health

Collagen is indeed found in some parts of the eye, including the cornea (outermost transparent layer), sclera (white outer layer), and vitreous humor (jelly-like substance filling the eye). It contributes to the structural integrity and transparency of the cornea, providing some support to the sclera, and contributing to the gel-like structure of the vitreous humor.
Collagen provides some protection against ultraviolet (UV) radiation damage to the eyes. UV exposure can lead to conditions like photokeratitis (sunburn of the cornea) and cataracts. Collagen supplementation may help strengthen the cornea and sclera, reducing susceptibility to UV-related damage. Also, it may help prevent or alleviate certain eye conditions associated with collagen degradation or dysfunction, such as keratoconus (corneal thinning), cataracts (clouding of the lens), and retinal detachment.
Recent posts
Nutrition
Nutrition
Liquorice Root: Benefits And Uses
You can spell it liquorice or licorice; this herb or root has been in use for centuries in most medicinal applications, as a natural sweetener and to enhance flavors. Regarding its origins, it comes from the root of the "Glycyrrhiza galbre" plant and...
Nutrition
Is Ramen Healthy? Here's What Dietician Says
Ramen is a traditional dish from Japan that in the recent era has become a global phenomenon. This beloved and comforting soupy dish however has been questioned, when it comes to its nutrition. Best for those looking for a quick (instant), affo...
Nutrition
Is Wheat Bread Healthy? An Expert Picks
Wheat bread has been proudly celebrated as a dietary staple in countless homes for as long as people can remember. It has earned a reputation as a healthier alternative to white or any other processed bread, that no one can deny. Because of its evide...
Nutrition
Is Sausages Healthy? Nutrition And Health Benefits
Sausages are tasty in an addictive way, making them one of the most popular foods worldwide. You may have enjoyed this convenient food often, whether on a bun with mustard or grilled on a barbecue, the simple preparation methods are what makes its co...
Nutrition
Ice Cream Benefits: Nutrition, Potential Risks And Best Choices
Not gonna lie, ice cream is often taken as a guilty pleasure treat, a delightful treat that takes you to cloud nine but is frequently associated with negative health implications. Nonetheless, the happy news is when devoured mindfully, ice cream can ...
Nutrition
Is Sushi Healthy? Some Good and Bad Choices
Sushi is a wholesome meal and a beloved Japanese dish. The traditional sushi recipe is a simple combination of fresh fish, vegetables, and vinegared rice which is popular for its minimalistic preparation. As with any food, there are factors that dete...







